All over the world cattle suffer from contagions of the hoofs. It very seriously concerns productivity of dairy cows. These diseases have a noticeable effect on the profitability dairy farms exactly. It was found out that these diseases have different causes. About 60 % of the cows are suffering from different hoofs deceases all over the world. .
In the majority of leg infection cases first symptoms of disease appear before 30 days when the cow begins to limp. Injuries speak for themselves. They are very painful, but they do not provoke the limp, but this pain is the cause of chronic stress. The animals become indisposed. Cortisole begins to work out. It has a negative impact on the immune system of the animals. Thus, the injury of hoof become real: decreases both food consumption and milk productivity, decreases immune system.
The first goal is to notice the cause and to find an effective way of solution. We have to understand which factors cause the illness. The real cause of leg illness could be pathogenic bacteria. When we recognized the problem, it is very easy to find a solution. Good preventive measures of the illnesses mean fewer cases of the injuries as such. Good result: happy cows – happy farmer!!!
Hoofs
The average rate of hoof growth in healthy cows is 1mm per week. It grows faster from the front. Forepart of sole becomes longer during the time when the heel does not grow. This factor is very important. Holstein cows have a negative heredity. They have a tendency to low heel presence. In the case when the hell is too low it touches the ground every time. Consequently it leads to hyper granulation. Perhaps, it could be called traumatic hair growth. The hyper granulation is very sensible to additional traumas. Inflammation take place when any infection is get into wound. Treatable therapy of these wounds and injuries is very difficult to reach, because cows are walking all the time.
That is why it is very important to start to cut hoof as early as at calf’s age of 6 months. It is easier to influence hoof structure in early calf’s age. Bad child’s shoes influence foot and walking during his adult life. Wrong form of hoof will influence whole exterior of milk cow.
Hoof horn growths with speed of 1mm per week and usually has very irregular wear. This results in uneven distribution of body weight pressure on the foot. Uneven pressure results in tension and cracks of hoof texture. This constant internal injury will be exposed to external infections, which will spread on hoof and create limp and pain as animal walks.
Cutting hoofs three times a year starting from early age is a first step in order to prevent contagions of hoofs.




 |
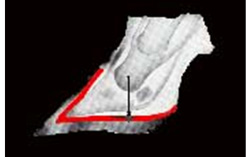
Heel is too low, high risk of traumatic hairy misgrowth. |
 |
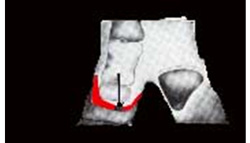
Virtually optimal cut. It indicates the necessity of regular cuts. If left without attention, situation will deteriorate in few weeks. |
 |
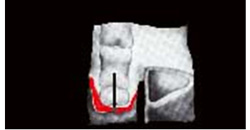
External line is too high, too much pressure on internal part. |
 |
Virtually optimal situation. |
Microorganisms causing contagions of hoofs.
There were defined few types of bacteria, which are potential aggressors against cow’s hoofs and feet. At the moment practically the only clear position is present, that to achieve infectious dangerous level and attack skin a group of few different bacteria is necessary.
Bacteroides spp, Spirochaetes spp, Camphylobacter Faecalis and Fusobacterium Necrophorum – all these bacteria usually live in the intestine of cattle stock. To survive in tough conditions of intestine they create a bio film around their colonies. When bacteria leave body with animal manure thanks to bio film they get a possibility to survive. The above mentioned bacteria are anaerobic, a film covering them is a protection from oxygen in cowsheds.
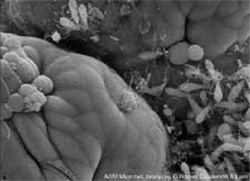
Inside the intestine. It can be seen a bio film with different bacteria, which build up a cluster (group).
Bio film – mucous membrane, sticky substance, which easily sticks to other organisms and any type of soil. It can and will stick to many surfaces and is open for many organisms, which are looking for a shelter. Cluster (group of bacteria) has good stable potential for attack on skin in very short period of time in animal manure, where there is enough of food for reproduction. The core of problem of contagions of hoofs ir eternal humidity of surface and great nourishing environment for development of bacteria.
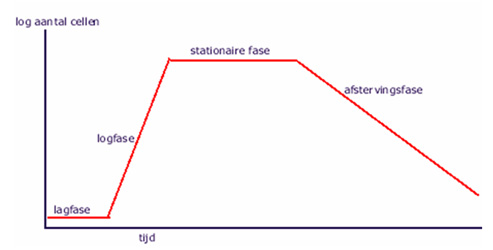
Being found in the conditions of cowsheds bacteria are forced to adapt their metabolism (metabolic processes) to new conditions of life. As soon as bacteria adapt explosive reproduction follows, which makes cluster (group) very strong for infectious attack, group soon achieves infection end and exceeds it.
Lower temperatures of the environment increase the time necessary for bacteria to achieve infection end.
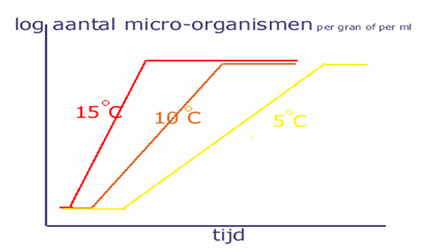
Cows walking in the cowshed permanently contact with their own manure. There are clusters in bio films present in this manure.

Different bacteria in cluster inside the bio film.
Manure contacts with skin of legs. Mucous components of bio film stick to skin. There is enough of food for reproduction of bacteria inside the bio film. After few hours they can achieve infectious end.
Bacteria create bio film for protecting own ecosystem. There are factors necessary for reproduction and survival inside the bio film.
Bacteria bred in laboratories and artificial conditions do not need such protection for reproduction, they are bred for real conditions of environment and nutrition, they do not need protection.
Bio film is also a protection against antibiotics and disinfectants. With bio film we need 200% more active substance of disinfectant or antibiotic in order to kill colony of pathogenic bacteria.
Infectious end is such amount of bacteria, which is necessary to cause diseases. For each type of bacteria the amount is different. The conditions can influence the infectious end: broken immune system of animal reduces the amount of bacteria, which can cause disease of animal organism.
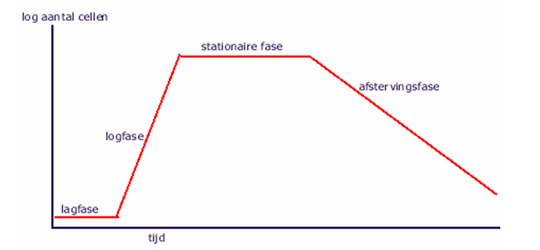
Weakening of immune system can be caused by different reasons.
Highly productive cows have problems with the source of energy during first 60 days of lactation. These and many other subclinical deviations in metabolism will weaken the immune system. Immune system will need vitamins and minerals for optimal conditions. After calving tripe (first section of ruminants stomach) needs time for adaptation of macterial ruminal flora to reinforced energetical ration. Acid producing flora is stable during few days, acid processing flora needs 3 weeks in order to achieve necessary level. As a result there is a high possibility of tripe acidosis. Tripe acidosis has negative impact on minerals and vitamins resorption in the tripe. As a result is broken immune system.
Veterinarian-consultant will determine negative energetical balance, evaluating condition of cows during first two months after calving. Each 5 litres of produced milk over the level of energy provided for a cow in the form of food is 1kg of lost weight of a cow. The analysis of ill-conditioned cows in the form of writing their condition during long time and comparison of this condition of body after 1 and 2 months of lactation provide information about energetical balance of animals. This is also a way of finding out if immune system of cows is suppressed. If immune system is suppressed, you will probably see few halting cows due to infectious diseases of cows.
 |
 |
Conditions 1, |
 |
 |
Conditions 3,5. |
 |
 |
Conditions 5. |
 |
Value 1 |
 |
Value 2. |
 |
Value 3. |
 |
Value 4. |
 |
Value 5. |
With adequate source of food bacteria also need moisture for survival. Air humidity can be mean transferring bacteria, which look for a place for creation of new colonies. Bacteria find necessary moisture in the cowsheds, produced by cows. Urine, remnants of milk, calf bed excretion etc. – these all are great sources of moisture. Necessary condition in the construction of cowsheds is very good ventilation. Dry surfaces in the dwellings of animals lower risk that colonies of pathogenic bacteria will reach infectious end.


What should be pointed our for risk analysis in cowsheds:
Conclusions: infectious diseases of hoofs are extremely difficult problem for solving because:
Result of infections of cow hoofs.
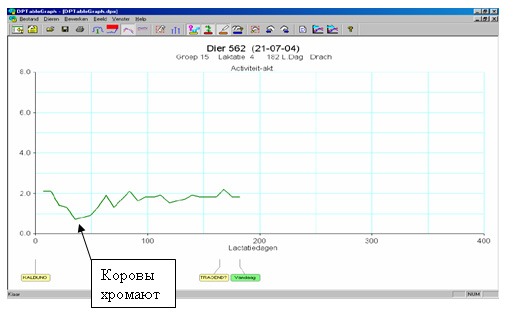
ЭThis graphic, „Vestfalia Surge Cow Plan”, shows activity of cows. Graphic shows that activity of cows is lowered in 30 days before cow starts really to limp. 30 days more are necessary for recovery. Thus activity lowers for 60 days.
Lowering of activity means:
How can we cope with huge problems in cow world.
1. We know that the majority of the most powerful pathogens is normal flora of cattle stomack. We cannot influence that.
2. We know that pathogens build bio film around own colonies in the stomach.
Being outside the body in the manure, pathogens (with bio film) colonize surfaces. We can influence this.
Cleaning of cowsheds means less manure. Less manure means less pathogens on the floor. Nevertheless manure ir present in cracks and pores of concrete. In these cracks pathogens create bio film and unite in dangerous clusters. These microscopically small pores are impossible to clean with normal cleaning agents, used in cowsheds.
Using non-pathogenic bacteria, which produce enzymes for liquidation of bio film, we can clean these dangerous places: pores and micro cracks in surfaces. After losing bio film non-pathogenic bacteria will try to create colonies in such deepening and pores. Non-pathogenic bacteria will use all available food environment for own reproduction. After using all available food – they will return to the form of spheres and will wait for new manure, so that again start reproduction. In such conditions there is no food for pathogenic bacteria.
This is the way, with the help of which we can hope to create floor without pathogens in cowsheds. The problem is that cows produce manure 24 hours a day. Emission of pathogens takes place 24 hours a day. We must assure conditions that our non-pathogenic bacteria permanently remain in majority. Sprinkling pores with solution of non-pathogenic bacteria, we can be sure that on the floor non-pathogenic bacteria have constant numeric supremacy during all the time.


Concrete under microscope is shown on the photography. Small pores are places, where pathogens can hide. There they find food for building bio film and reproduction, create stable dangerous clusters.
3. Constantly present manure will stick to skin and hoofs of cows. Bio film, mucus of dangerous clusters will stick to skin. These clusters will produce substances destroying cells of skin. Door is open for pathogens to enter the body and destroy fibre under the skin. Inflammation will start.
We can influence this
Using non-pathogenic bacteria in trough for feet or spraying on feet solution of non-pathogenic bacteria, we can reach that skin will be colonized (covered with colonies) destroying bio film by non-pathogenic bacteria. To be sure that they constantly leave the majority it is necessary to use solution twice a day. Pathogens without bio film have no chance to find conditions for reproduction. All nutritious environment will be used by non-pathogenic bacteria. Nutritious energy of manure will go to reproduction of non-pathogenic bacteria, but feet and hoofs will be dry and clean.
Conclusion:
Using non-pathogenic bacteria from the class Bacillus we can suppress growth of bio film and make floors in cowshed relatively non pathogenic. Using other kinds from this class we can clean skin and hoof, make them dry and prevent dermatitis of extremities.
|
© 2008-2010 ООО «NANOPROTEC» |
Тел.: (371) 67240484 |
|